ROS2服务通信
官方文档链接:了解服务
1. 服务的概念
1.1 概念介绍
服务分为客户端和服务端,平时我们用的手机APP都可以成为客户端,而APP服务器对于软件来说就是服务端。 具体流程包括客户端发送请求给服务端,服务端可以根据客户端的请求做一些处理,然后返回结果给客户端。所以服务-客户端模型,也可以成为请求-响应模型。 如不理解请看动图: 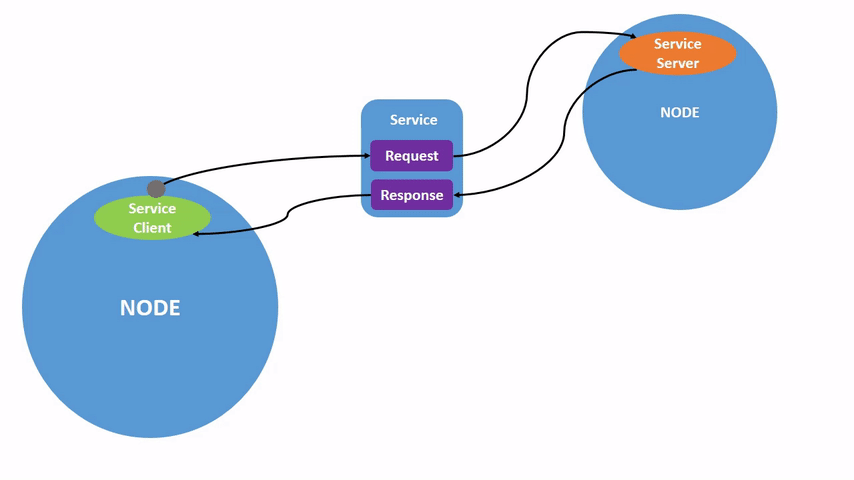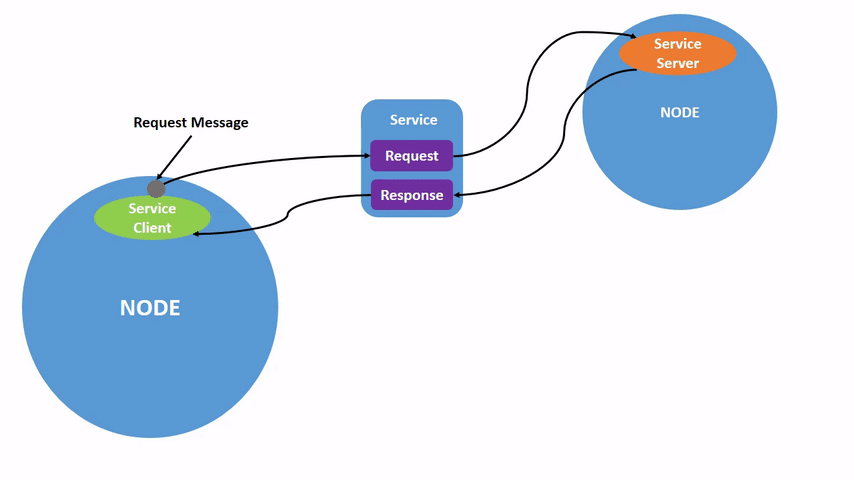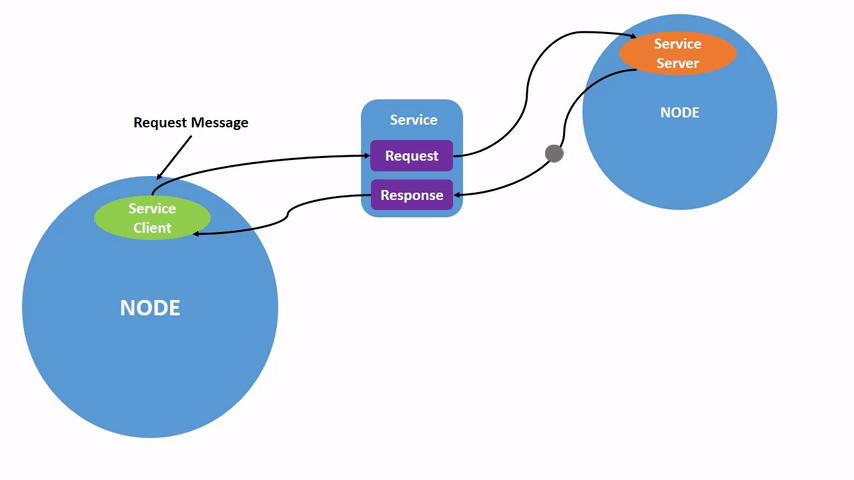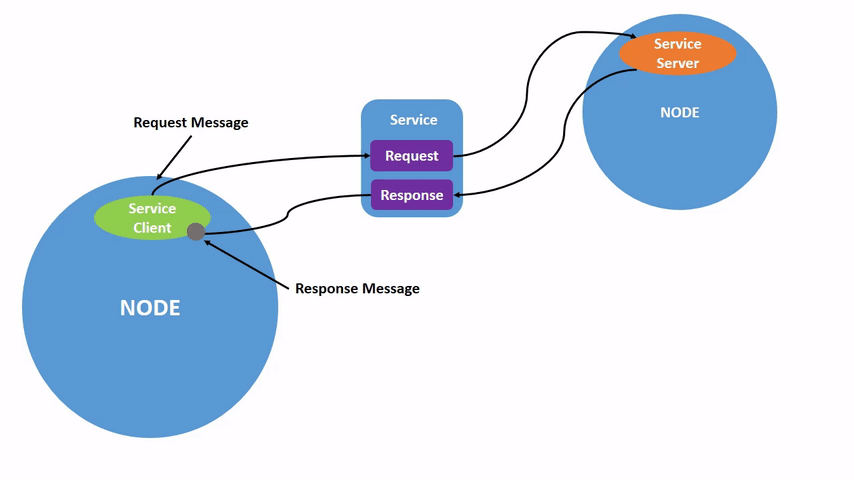
1.2 服务的特点
上一章我们介绍了ROS2的话题通信,那么服务通信和话题通信有什么区别呢?是有的,服务通信和话题通信的区别在于:
- 同一个服务只能有一个服务端,但是可以有多个客户端,但是话题通信没有这个限制。
- 服务通信是一对一的通信,客户端发送请求给服务端,服务端返回结果给对应客户端,而话题通信是一对多的通信,发布者发布消息,所有的订阅者都可以接收到消息。
一种通俗的理解:
- 外卖餐馆是服务端,客户是客户端,可以有多个客户(client)同时点餐(request),每个客户点餐后,餐馆(server)做菜并通过外卖小哥送回客户所点的菜品(response)。你点餐就做菜,不点餐就不做菜,这就是服务通信。
- 而话题通信相当于你去学校食堂吃快餐。学校的食堂(publisher),根据统一的配方(interface)做好快餐(topic)并在窗口发布(publish),你(subscriber)可以选择吃(subscribe)或者不吃,但是食堂会一直批量生产快餐,不会因为你不吃而停止生产。
1.3 应用场景
服务通信的概念在机器人控制上的应用有很多,以下是一些常见的可以通过服务-客户端任务构建的机器人任务:
- 哨兵机器人导航:机器人通过服务请求导航节点,导航节点返回机器人的导航路径。
- 工程机器人机械臂抓取:机器人本体通过客户端请求机械臂节点完成抓取任务,机械臂节点返回抓取结果(成功/失败)。 一般来说,服务通信适用于一些需要请求-响应的任务,这种任务一般来说是非周期性的,是根据需要偶尔执行的任务。由于服务通信的请求和响应有一定的延迟,所以尽量不要使用服务通信来实现实时通信。 而话题通信适用于一些需要实时传输数据的任务,这种任务一般是周期性的,比如机器人关节角度的实时发布,激光雷达的实时数据发布等。
2. 服务的实现
2.1 服务接口定义
服务的接口定义和话题的接口定义类似,也是通过IDL文件来定义的。话题通信的IDL文件是.msg文件,而服务通信的IDL文件是.srv文件。服务在 ROS 包的 'srv/' 目录下的 '.srv' 文件中进行描述和定义。
一个服务描述文件由请求和响应的消息类型组成,用 '---' 分隔。任何两个 '.msg' 文件通过 '---' 连接在一起都构成一个合法的服务描述。
下面是一个简单的服务接口定义的例子:
ros2 pkg create example_interfaces --build-type ament_cmake --dependencies rosidl_default_generators builtin_interfaces以下是代码:
# example_interfaces/srv/AddTwoInts.srv
int64 a
int64 b
---
int64 sumcmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.8)
project(example_interfaces)
if(CMAKE_COMPILER_IS_GNUCXX OR CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID MATCHES "Clang")
add_compile_options(-Wall -Wextra -Wpedantic)
endif()
# find dependencies
find_package(ament_cmake REQUIRED)
find_package(rosidl_default_generators REQUIRED)
find_package(builtin_interfaces REQUIRED)
rosidl_generate_interfaces(${PROJECT_NAME}
"srv/AddTwoInts.srv"
DEPENDENCIES builtin_interfaces// [!code focus]
)// [!code focus]
if(BUILD_TESTING)
find_package(ament_lint_auto REQUIRED)
# the following line skips the linter which checks for copyrights
# comment the line when a copyright and license is added to all source files
set(ament_cmake_copyright_FOUND TRUE)
# the following line skips cpplint (only works in a git repo)
# comment the line when this package is in a git repo and when
# a copyright and license is added to all source files
set(ament_cmake_cpplint_FOUND TRUE)
ament_lint_auto_find_test_dependencies()
endif()
ament_package()<?xml version="1.0"?>
<?xml-model href="http://download.ros.org/schema/package_format3.xsd" schematypens="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"?>
<package format="3">
<name>example_interfaces</name>
<version>0.0.0</version>
<description>TODO: Package description</description>
<maintainer email="[email protected]">shidong</maintainer>
<license>TODO: License declaration</license>
<buildtool_depend>ament_cmake</buildtool_depend>
<depend>rosidl_default_generators</depend>
<depend>builtin_interfaces</depend>
<member_of_group>rosidl_interface_packages</member_of_group>// [!code focus]
<test_depend>ament_lint_auto</test_depend>
<test_depend>ament_lint_common</test_depend>
<export>
<build_type>ament_cmake</build_type>
</export>
</package>上面的例子定义了一个服务接口,请求消息类型是两个 int64 类型的数据 a 和 b,响应消息类型是一个 int64 类型的数据 sum。这个服务的作用是将 a 和 b 相加,然后返回结果 sum。
回到工作空间目录进行编译
colcon build --allow-overriding example_interfacessource install/setup.bash通过以下命令查看生成的服务接口
ros2 interface show example_interfaces/srv/AddTwoInts如果一切正常,你会看到以下输出:
# example_interfaces/srv/AddTwoInts.srv
int64 a
int64 b
---
int64 sum2.2服务端实现
服务端的实现和话题的发布者实现类似,也是通过创建一个节点,然后创建一个服务来实现的。下面是一个简单的服务端实现的例子: 在src目录下构建服务端接口功能包:
ros2 pkg create example_service --build-type ament_cmake --dependencies rclcpp example_interfaces以下是代码:
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp" // 包含ROS 2核心库的头文件
#include "example_interfaces/srv/add_two_ints.hpp" // 包含AddTwoInts服务的定义
// 定义一个类AddTwoIntsServer继承自rclcpp::Node,用于实现服务节点
class AddTwoIntsServer : public rclcpp::Node
{
public:
// 构造函数
AddTwoIntsServer()
: Node("add_two_ints_server") // 初始化父类Node,并命名节点为"add_two_ints_server"
{
// 创建一个服务对象
// 参数1: 服务名称 "add_two_ints"
// 参数2: 服务处理函数,使用std::bind绑定成员函数handle_service
service_ = this->create_service<example_interfaces::srv::AddTwoInts>(
"add_two_ints",
std::bind(&AddTwoIntsServer::handle_service, this, std::placeholders::_1, std::placeholders::_2));
// 在日志中输出服务已启动的提示信息
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Service is ready to add two integers.");
}
private:
// 服务处理函数
// 参数1: 客户端请求的指针,包含两个整型数a和b
// 参数2: 服务响应的指针,用于返回计算结果sum
void handle_service(
const std::shared_ptr<example_interfaces::srv::AddTwoInts::Request> request,
std::shared_ptr<example_interfaces::srv::AddTwoInts::Response> response)
{
// 将客户端发送的两个整型数相加,并将结果赋值给响应中的sum字段
response->sum = request->a + request->b;
// 打印接收到的请求和发送的响应日志
RCLCPP_INFO(
this->get_logger(),
"Incoming request: a=%ld, b=%ld; Sending response: sum=%ld",
request->a, request->b, response->sum);
}
// 服务对象的共享指针,用于管理服务的生命周期
rclcpp::Service<example_interfaces::srv::AddTwoInts>::SharedPtr service_;
};
// 主函数
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
// 初始化ROS 2客户端库
rclcpp::init(argc, argv);
// 创建AddTwoIntsServer节点并启动服务
rclcpp::spin(std::make_shared<AddTwoIntsServer>());
// ROS 2关闭时清理资源
rclcpp::shutdown();
return 0;
}cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.8)
project(example_service)
if(CMAKE_COMPILER_IS_GNUCXX OR CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID MATCHES "Clang")
add_compile_options(-Wall -Wextra -Wpedantic)
endif()
# find dependencies
find_package(ament_cmake REQUIRED)
find_package(rclcpp REQUIRED)
find_package(example_interfaces REQUIRED)
add_executable(add_two_ints_server src/add_two_ints_server.cpp) // [!code focus]
ament_target_dependencies(add_two_ints_server rclcpp example_interfaces) // [!code focus]
install(TARGETS // [!code focus]
add_two_ints_server // [!code focus]
DESTINATION lib/${PROJECT_NAME}) // [!code focus]
if(BUILD_TESTING)
find_package(ament_lint_auto REQUIRED)
# the following line skips the linter which checks for copyrights
# comment the line when a copyright and license is added to all source files
set(ament_cmake_copyright_FOUND TRUE)
# the following line skips cpplint (only works in a git repo)
# comment the line when this package is in a git repo and when
# a copyright and license is added to all source files
set(ament_cmake_cpplint_FOUND TRUE)
ament_lint_auto_find_test_dependencies()
endif()
ament_package()<?xml version="1.0"?>
<?xml-model href="http://download.ros.org/schema/package_format3.xsd" schematypens="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"?>
<package format="3">
<name>example_service</name>
<version>0.0.0</version>
<description>TODO: Package description</description>
<maintainer email="[email protected]">shidong</maintainer>
<license>TODO: License declaration</license>
<buildtool_depend>ament_cmake</buildtool_depend>
<depend>rclcpp</depend>
<depend>example_interfaces</depend>
<test_depend>ament_lint_auto</test_depend>
<test_depend>ament_lint_common</test_depend>
<export>
<build_type>ament_cmake</build_type>
</export>
</package>写好代码后,编译节点:
colcon build --allow-overriding example_interfacessource install/setup.bash运行服务端节点:
ros2 run example_service add_two_ints_server服务端会输出服务已启动的提示信息,类似如下:
[INFO] [1734720047.138933760] [add_two_ints_server]: Service is ready to add two integers.我们可以通过 ros2 service list 命令查看当前运行的服务:
ros2 service list如果一切正常,你会看到以下输出,说明服务已经运行:
/add_two_ints
/add_two_ints_server/describe_parameters
/add_two_ints_server/get_parameter_types
/add_two_ints_server/get_parameters
/add_two_ints_server/list_parameters
/add_two_ints_server/set_parameters
/add_two_ints_server/set_parameters_atomically其中 /add_two_ints 是我们创建的服务,/add_two_ints_server/describe_parameters 等是 ROS 2 内部的服务,用于参数管理。
我们目前没有编写客户端,所以我们现在使用 ros2 service call 命令手动发送请求,来模拟客户端发送请求。例如将 a=10 和 b=20 发送到服务端:
ros2 service call /add_two_ints example_interfaces/srv/AddTwoInts "{a: 10, b: 20}"服务端会输出请求和响应的信息,类似如下:
requester: making request: example_interfaces.srv.AddTwoInts_Request(a=10, b=20)
response:
example_interfaces.srv.AddTwoInts_Response(sum=30)说明服务端已经成功接收到请求,并返回了计算结果 sum=30。
2.3 客户端实现
客户端的实现和话题的订阅者实现类似,也是通过创建一个节点,然后创建一个客户端来实现的。下面是一个简单的客户端实现的例子:
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp" // ROS 2 核心头文件
#include "example_interfaces/srv/add_two_ints.hpp" // 服务定义头文件
class AddTwoIntsClient : public rclcpp::Node
{
public:
AddTwoIntsClient()
: Node("add_two_ints_client") // 初始化父类Node,并命名为"add_two_ints_client"
{
// 创建一个客户端对象,指定服务类型和名称
client_ = this->create_client<example_interfaces::srv::AddTwoInts>("add_two_ints");
}
// 向服务发送请求并获取结果
int64_t send_request(int64_t a, int64_t b)
{
// 等待服务可用
while (!client_->wait_for_service(std::chrono::seconds(5)))
{
if (!rclcpp::ok()) // 如果节点被终止,退出等待
{
RCLCPP_ERROR(this->get_logger(), "Interrupted while waiting for the service. Exiting.");
return -1;
}
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Service not available, waiting again...");
}
// 创建请求对象
auto request = std::make_shared<example_interfaces::srv::AddTwoInts::Request>();
request->a = a;
request->b = b;
// 发送请求并等待响应
auto result_future = client_->async_send_request(request);
if (rclcpp::spin_until_future_complete(this->get_node_base_interface(), result_future) ==
rclcpp::FutureReturnCode::SUCCESS)
{
// 获取服务响应
auto response = result_future.get();
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Received response: sum=%ld", response->sum);
return response->sum;
}
else
{
RCLCPP_ERROR(this->get_logger(), "Failed to call service add_two_ints.");
return -1;
}
}
private:
// 客户端对象的共享指针,用于管理客户端的生命周期
rclcpp::Client<example_interfaces::srv::AddTwoInts>::SharedPtr client_;
};
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
// 初始化ROS 2
rclcpp::init(argc, argv);
// 创建AddTwoIntsClient节点
auto client_node = std::make_shared<AddTwoIntsClient>();
// 定义要发送的参数
int64_t a = 10;
int64_t b = 20;
// 调用服务并接收响应
int64_t sum = client_node->send_request(a, b);
// 如果调用成功,打印结果
if (sum != -1)
{
RCLCPP_INFO(client_node->get_logger(), "Sum of %ld and %ld is %ld", a, b, sum);
}
// 关闭ROS 2
rclcpp::shutdown();
return 0;
}cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.8)
project(example_service)
if(CMAKE_COMPILER_IS_GNUCXX OR CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID MATCHES "Clang")
add_compile_options(-Wall -Wextra -Wpedantic)
endif()
# find dependencies
find_package(ament_cmake REQUIRED)
find_package(rclcpp REQUIRED)
find_package(example_interfaces REQUIRED)
add_executable(add_two_ints_server src/add_two_ints_server.cpp)
ament_target_dependencies(add_two_ints_server rclcpp example_interfaces)
add_executable(add_two_ints_client src/add_two_ints_client.cpp)// [!code focus]
ament_target_dependencies(add_two_ints_client rclcpp example_interfaces)// [!code focus]
install(TARGETS
add_two_ints_server
add_two_ints_client// [!code focus]
DESTINATION lib/${PROJECT_NAME})
if(BUILD_TESTING)
find_package(ament_lint_auto REQUIRED)
# the following line skips the linter which checks for copyrights
# comment the line when a copyright and license is added to all source files
set(ament_cmake_copyright_FOUND TRUE)
# the following line skips cpplint (only works in a git repo)
# comment the line when this package is in a git repo and when
# a copyright and license is added to all source files
set(ament_cmake_cpplint_FOUND TRUE)
ament_lint_auto_find_test_dependencies()
endif()
ament_package()写好代码后,编译节点:
colcon build --allow-overriding example_interfacessource install/setup.bash先运行服务端节点,然后运行客户端节点:
ros2 run example_service add_two_ints_serverros2 run example_service add_two_ints_client客户端会发送请求到服务端,服务端会返回计算结果,客户端会打印出计算结果,类似如下:
[INFO] [1734687434.059710704] [add_two_ints_client]: Received response: sum=30
[INFO] [1734687434.059772158] [add_two_ints_client]: Sum of 10 and 20 is 30至此,服务端和客户端的实现就完成了。 在这个例子中,我们通过服务通信实现了一个简单的加法服务,客户端发送两个整型数 a 和 b 到服务端,服务端将 a 和 b 相加,然后返回结果 sum 给客户端。这个例子展示了服务通信的基本流程,你可以根据自己的需求来定义更复杂的服务接口和实现。